Synonyms for atomic number 82 a soft heavy toxic malleable metallic element Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the. What is atomic mass for Pb-208 isotope? Answer: 207.97665 Da. What is isotopic mass for Pb-208 isotope? Answer: 207.97665. How many neutrons does Pb-208 isotope have? How many protons does Pb-208 isotope have? How many electrons does Pb-208 isotope have? What is atomic number for Pb-208 isotope?
The Element Lead
[Click for Isotope Data]

Atomic Number: 82
Atomic Weight: 207.2
Melting Point: 600.61 K (327.46°C or 621.43°F)
Boiling Point: 2022 K (1749°C or 3180°F)
Density: 11.342 grams per cubic centimeter
Phase at Room Temperature: Solid
Element Classification: Metal
Period Number: 6
Group Number: 14
Group Name: none
What's in a name? From the Anglo-Saxon word lead. Lead's chemical symbol comes from the Latin word for waterworks, plumbum.
Say what? Lead is pronounced as LED.
History and Uses:
Lead has been known since ancient times. It is sometimes found free in nature, but is usually obtained from the ores galena (PbS), anglesite (PbSO4), cerussite (PbCO3) and minum (Pb3O4). Although lead makes up only about 0.0013% of the earth's crust, it is not considered to be a rare element since it is easily mined and refined. Most lead is obtained by roasting galena in hot air, although nearly one third of the lead used in the United States is obtained through recycling efforts.
Lead is a soft, malleable and corrosion resistant material. The ancient Romans used lead to make water pipes, some of which are still in use today. Unfortunately for the ancient Romans, lead is a cumulative poison and the decline of the Roman empire has been blamed, in part, on lead in the water supply. Lead is used to line tanks that store corrosive liquids, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4). Lead's high density makes it useful as a shield against X-ray and gamma-ray radiation and is used in X-ray machines and nuclear reactors. Lead is also used as a covering on some wires and cables to protect them from corrosion, as a material to absorb vibrations and sounds and in the manufacture of ammunition. Most of the lead used today is used in the production on lead-acid storage batteries, such as the batteries found in automobiles.
Several lead alloys are widely used. Solder, an alloy that is nearly half lead and half tin, is a material with a relatively low melting point that is used to join electrical components, pipes and other metallic items. Type metal, an alloy of lead, tin and antimony, is a material used to make the type used in printing presses and plates. Babbit metal, another lead alloy, is used to reduce friction in bearings.
Lead forms many useful compounds. Lead monoxide (PbO), also known as litharge, is a yellow solid that is used to make some types of glass, such as lead crystal and flint glass, in the vulcanizing of rubber and as a paint pigment. Lead dioxide (PbO2) is a brown material that is used in lead-acid storage batteries. Trilead tetraoxide (Pb3O4), also known as red lead, is used to make a reddish-brown paint that prevents rust on outdoor steel structures. Lead arsenate (Pb3(AsO4)2) has been used as an insecticide although other, less harmful, substances have now largely replaced it. Lead carbonate (PbCO3), also known as cerussite, is a white, poisonous substance that was once widely used as a pigment for white paint. Use of lead carbonate in paints has largely been stopped in favor of titanium oxide (TiO2). Lead sulfate (PbSO4), also known as anglesite, is used in a paint pigment known as sublimed white lead. Lead chromate (PbCrO4), also known as crocoite, is used to produce chrome yellow paint. Lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) is used to make fireworks and other pyrotechnics. Lead silicate (PbSiO3) is used to make some types of glass and in the production of rubber and paints.
Estimated Crustal Abundance: 1.4×101 milligrams per kilogram
Estimated Oceanic Abundance: 3×10-5 milligrams per liter
Number of Stable Isotopes: 3 (View all isotope data)
What Is Atomic Number 82
Ionization Energy: 7.417 eV
Oxidation States: +4, +2
Atomic Number 82 Means
Electron Shell Configuration: | 1s2 |
2s2 2p6 | |
3s2 3p6 3d10 | |
4s2 4p6 4d10 4f14 | |
5s2 5p6 5d10 | |
6s2 6p2 |
Atomic Number 82 Metallic Element

For questions about this page, please contact Steve Gagnon.
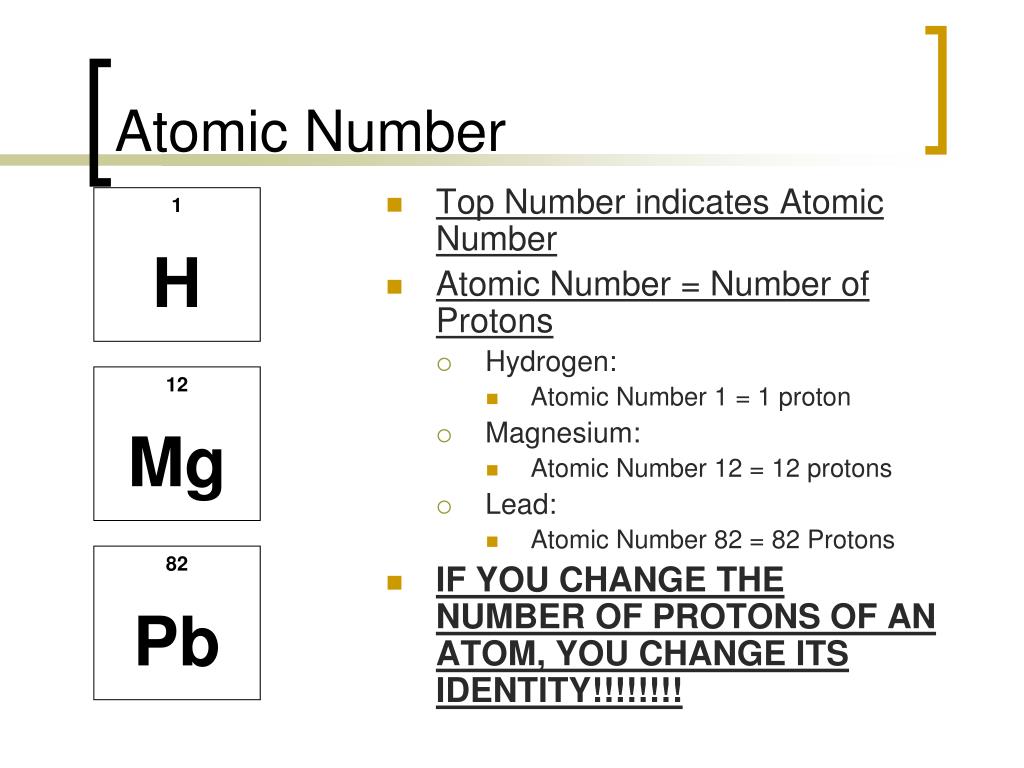
We remember from our school chemistry course that every element has its own specific atomic number. It is the same as the number of protons that the atom of each element has, so sometimes atomic number is called proton number. It is always the whole number and it ranges from 1 to 118, according to the number of the element in the Periodic Table. This number can be really important and something essential to know, in relation to a certain chemical element which is the issue of our interest at the moment.
Why is this so? Why is the atomic number so important? First of all, it is the number that makes elements different from one another as it shows the number of protons in their nuclei. Also, knowing the atomic number of an element can give us an idea about the position of the element in the Periodic Table. Atomic number of an element never changes: for example, the atomic number of oxygen is always 8, and the atomic number of Chlorine is always 18. The atomic number is marked with the symbol Z, taken from a German word zahl (or atomzahl, which is 'atomic number' in German).
This website is created for those who need to know the atomic number of a central chemical element. By using our website, you can do it in just one click and receive short and correct information on this matter. There is also some extra summary on every each chemical element which can be found at our website, including the atomic weight of each element, as well as physical and chemical properties of every element and its importance. Use this website at any time when you need to get fast and precise information about atomic or proton number of chemical elements.
List of chemical elements in periodic table with atomic number, chemical symbol and atomic weight. You can sort the elements by clicking on the table headers. Please click on the element name for complete list of element properties.
| Atomic Number | Chemical Symbol | Element Name | Atomic Weight (u) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | 1.008 |
| 2 | He | Helium | 4.003 |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | 6.94 |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | 9.012 |
| 5 | B | Boron | 10.81 |
| 6 | C | Carbon | 12.011 |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | 14.007 |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | 15.999 |
| 9 | F | Fluorine | 18.998 |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | 20.18 |
| 11 | Na | Sodium | 22.99 |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | 24.305 |
| 13 | Al | Aluminium | 26.982 |
| 14 | Si | Silicon | 28.085 |
| 15 | P | Phosphorus | 30.974 |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | 32.06 |
| 17 | Cl | Chlorine | 35.45 |
| 18 | Ar | Argon | 39.948 |
| 19 | K | Potassium | 39.098 |
| 20 | Ca | Calcium | 40.078 |
| 21 | Sc | Scandium | 44.956 |
| 22 | Ti | Titanium | 47.867 |
| 23 | V | Vanadium | 50.942 |
| 24 | Cr | Chromium | 51.996 |
| 25 | Mn | Manganese | 54.938 |
| 26 | Fe | Iron | 55.845 |
| 27 | Co | Cobalt | 58.933 |
| 28 | Ni | Nickel | 58.693 |
| 29 | Cu | Copper | 63.546 |
| 30 | Zn | Zinc | 65.38 |
| 31 | Ga | Gallium | 69.723 |
| 32 | Ge | Germanium | 72.63 |
| 33 | As | Arsenic | 74.922 |
| 34 | Se | Selenium | 78.971 |
| 35 | Br | Bromine | 79.904 |
| 36 | Kr | Krypton | 83.798 |
| 37 | Rb | Rubidium | 85.468 |
| 38 | Sr | Strontium | 87.62 |
| 39 | Y | Yttrium | 88.906 |
| 40 | Zr | Zirconium | 91.224 |
| 41 | Nb | Niobium | 92.906 |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 95.95 |
| 43 | Tc | Technetium | 98 |
| 44 | Ru | Ruthenium | 101.07 |
| 45 | Rh | Rhodium | 102.906 |
| 46 | Pd | Palladium | 106.42 |
| 47 | Ag | Silver | 107.868 |
| 48 | Cd | Cadmium | 112.414 |
| 49 | In | Indium | 114.818 |
| 50 | Sn | Tin | 118.71 |
| 51 | Sb | Antimony | 121.76 |
| 52 | Te | Tellurium | 127.6 |
| 53 | I | Iodine | 126.904 |
| 54 | Xe | Xenon | 131.293 |
| 55 | Cs | Caesium | 132.905 |
| 56 | Ba | Barium | 137.327 |
| 57 | La | Lanthanum | 138.905 |
| 58 | Ce | Cerium | 140.116 |
| 59 | Pr | Praseodymium | 140.908 |
| 60 | Nd | Neodymium | 144.242 |
| 61 | Pm | Promethium | 145 |
| 62 | Sm | Samarium | 150.36 |
| 63 | Eu | Europium | 151.964 |
| 64 | Gd | Gadolinium | 157.25 |
| 65 | Tb | Terbium | 158.925 |
| 66 | Dy | Dysprosium | 162.5 |
| 67 | Ho | Holmium | 164.93 |
| 68 | Er | Erbium | 167.259 |
| 69 | Tm | Thulium | 168.934 |
| 70 | Yb | Ytterbium | 173.045 |
| 71 | Lu | Lutetium | 174.967 |
| 72 | Hf | Hafnium | 178.49 |
| 73 | Ta | Tantalum | 180.948 |
| 74 | W | Tungsten | 183.84 |
| 75 | Re | Rhenium | 186.207 |
| 76 | Os | Osmium | 190.23 |
| 77 | Ir | Iridium | 192.217 |
| 78 | Pt | Platinum | 195.084 |
| 79 | Au | Gold | 196.967 |
| 80 | Hg | Mercury | 200.592 |
| 81 | Tl | Thallium | 204.38 |
| 82 | Pb | Lead | 207.2 |
| 83 | Bi | Bismuth | 208.98 |
| 84 | Po | Polonium | 209 |
| 85 | At | Astatine | 210 |
| 86 | Rn | Radon | 222 |
| 87 | Fr | Francium | 223 |
| 88 | Ra | Radium | 226 |
| 89 | Ac | Actinium | 227 |
| 90 | Th | Thorium | 232.038 |
| 91 | Pa | Protactinium | 231.036 |
| 92 | U | Uranium | 238.029 |
| 93 | Np | Neptunium | 237 |
| 94 | Pu | Plutonium | 244 |
| 95 | Am | Americium | 243 |
| 96 | Cm | Curium | 247 |
| 97 | Bk | Berkelium | 247 |
| 98 | Cf | Californium | 251 |
| 99 | Es | Einsteinium | 252 |
| 100 | Fm | Fermium | 257 |
| 101 | Md | Mendelevium | 258 |
| 102 | No | Nobelium | 259 |
| 103 | Lr | Lawrencium | 266 |
| 104 | Rf | Rutherfordium | 267 |
| 105 | Db | Dubnium | 268 |
| 106 | Sg | Seaborgium | 269 |
| 107 | Bh | Bohrium | 270 |
| 108 | Hs | Hassium | 277 |
| 109 | Mt | Meitnerium | 278 |
| 110 | Ds | Darmstadtium | 281 |
| 111 | Rg | Roentgenium | 282 |
| 112 | Cn | Copernicium | 285 |
| 113 | Nh | Nihonium | 286 |
| 114 | Fl | Flerovium | 289 |
| 115 | Mc | Moscovium | 290 |
| 116 | Lv | Livermorium | 293 |
| 117 | Ts | Tennessine | 294 |
| 118 | Og | Oganesson | 294 |
Lists of Elements in Periodic Table
You can also list the elements in various ordered properties with printable tables below.
Atomic Number Chart
Lists of Elements by Group Number in Periodic Table
Lead Element Chemical Series
» Group 1» Group 2» Group 3» Group 4» Group 5» Group 6» Group 7» Group 8» Group 9» Group 10» Group 11» Group 12» Group 13» Group 14» Group 15» Group 16» Group 17» Group 18